Drones have been around for a while now, used actively in the AEC (Architecture, Engineering & Construction) industry for aerial mapping, site and asset inspections, surveys, project marketing and more.
These flying cameras are accessible, convenient, and a great alternative to manual site inspections or helicopters.
Table of Contents
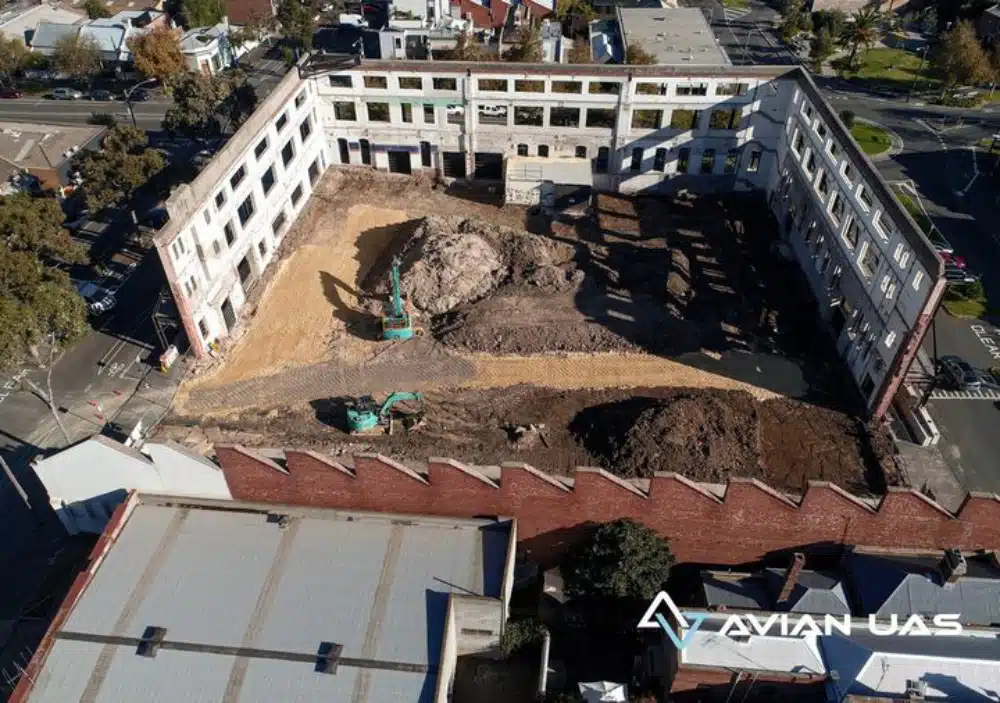
In recent years, drone technology has quickly evolved and has now become an integral part of the end-to-end construction process. From the initial site feasibility to tracking worksite productivity, stockpile calculations, identifying project bottlenecks or design flaws – drones help with all these tasks and so much more.
Here are a few pros and cons of using UAVs for surveying and mapping that every AEC professional must know.
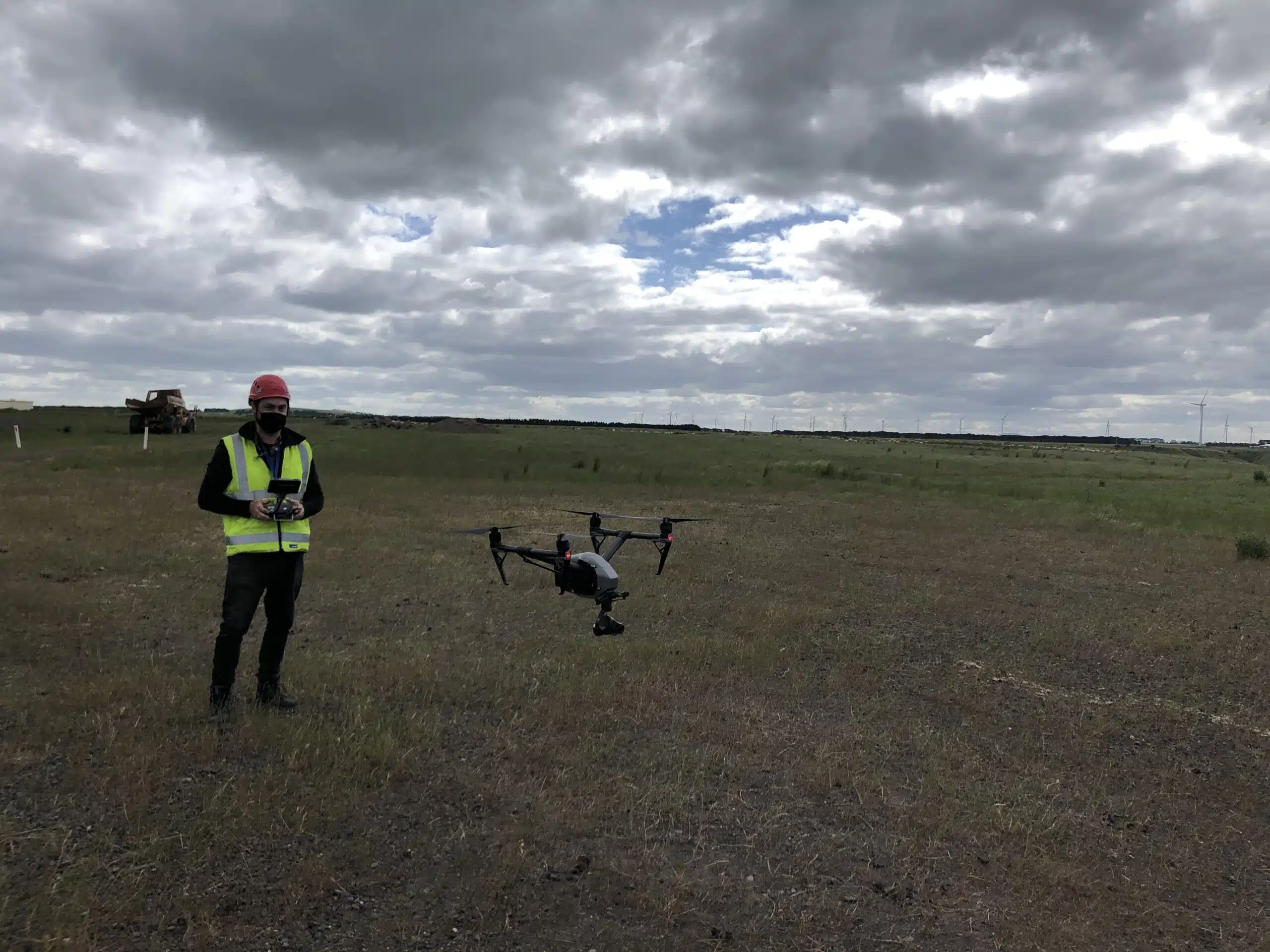

Pros of UAV Surveys
Capture live site record
Drones help project managers and builders access real-time footage of the site and project status. It helps in tracking project status, capturing worksite productivity and communicating to stakeholders.
Drones record site footage from live UAV surveys and can even stream it live to the laptop or tablet in real time. In this way you can access live site footage from the comfort of your office or mobile phone. This also reduces the need for repeated onsite visits and inspections.
Reduce worksite accidents
Drones reduce the risk of worksite accidents and fatal injuries. By using an aerial camera to assess or inspect existing conditions during a UAV survey, you can avoid human intervention unless absolutely necessary. Rather than having limited or no information about the existing conditions at heights, over large areas or above water, the drone operator can control the flight path, covering all the areas you want to capture.
Drones can easily reach inaccessible areas around the site during a UAV survey, including high towers, ceiling steelwork, underground pipelines, chimneys, etc. Many types of inspections have become safer, faster and more convenient with aerial surveying methods using drones.
Less human intervention
The drone requires little to no human involvement, unlike other surveying techniques. The drone pilot operates the drones from the ground, and the drone footage is recorded or directly streamed to a live video feed. There is less need to manually walk the ground and take hundreds of observations as is required with more traditional surveying methods.
This type of aerial surveying process reduces the risk of incidents and still ensures maximum data accuracy.

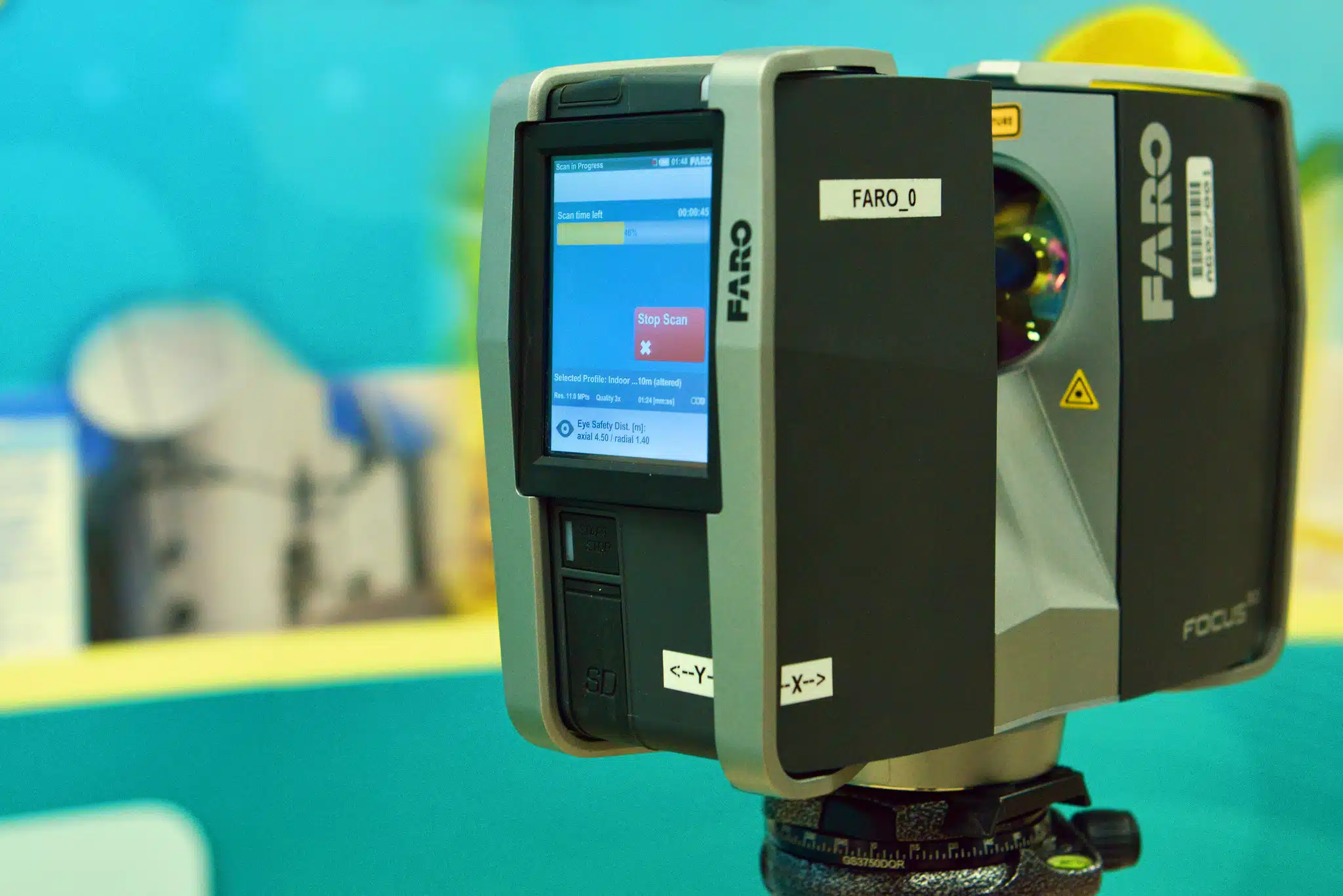
Drone data accuracy
Using the right approach, equipment and independent checks drones can deliver accuracy of 10-20mm. The required accuracy is entirely dependent on your unique project requirements however the delivered accuracy is dependent on the equipment and the surveying methodology employed by the surveyor or drone operator.
With drone mapping you will commonly hear about two types of accuracy:
Relative Accuracy and Absolute Accuracy
Relative Accuracy
Is the accuracy of two points or features relative to each other within the map/model but not in the real world. For example, if two points are measured and have the same distance as in reality then the relative accuracy of the map/model is high.
Absolute Accuracy
Is the accuracy of points and/or features in the map/model relative to their position in the real world in a certain reference frame. For example, if the position of a building is close to its actual position on the Earth, then the absolute accuracy is high.
Ground Sampling Distance (GSD)
Is the distance between the centre of adjacent pixels if measured on the ground. Put simply, the GSD is the size of one pixel representing the ground. For example, if the GSD is 2.5cm then each pixel represents 2.5cm of distance on the ground (2.5cm x 2.5cm = 6.25 square cm). So the larger the GSD value, the less resolution and therefore less visible details.
The GSD is directly affected by altitude of the UAV during the flight and especially over undulating terrain as the GSD will vary across the mapped area. Also the camera sensor, sensor quality, image noise and weather conditions can also affect the GSD value.
At Avian Australia, we use commercial grade equipment and qualified surveyors to provide our clients with commercial survey-grade results (+/- 10mm). If clients require a higher level of accuracy we can accommodate them according to our clients unique project requirements.
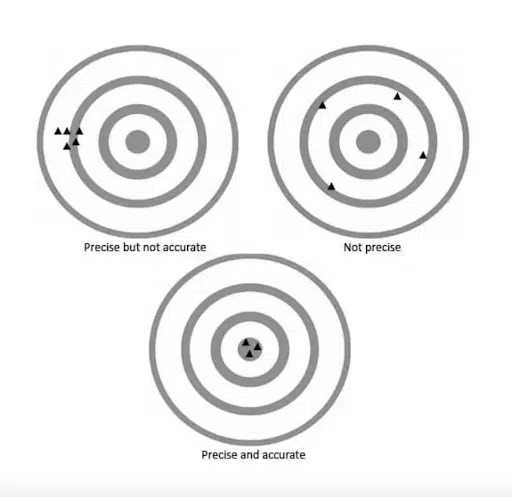
Image source: Photomodeler.com
At Avian Australia, we conduct a virtual site assessment (and often a physical one) to ensure understanding of your project requirements and expectations before proposing and quoting for a UAV Survey.
Identify building flaws
Drone surveying is a part of every step in the construction process. It also helps engineers identify any errors or structural flaws in the design and build.
With drones, it becomes easier to identify that thus rectify these errors before completion. This saves a lot of time and resources down the line as problems are solved earlier and at less cost than after handover.
More data and faster site inspections
Drones can inspect hundreds of acres in a single day. Our workflow often involves the aerial mapping of around 100ha in single day. Using drones helps to cover larger land areas and get survey-grade results from the combination of photogrammetry and surveying techniques.
The alternative, manual inspections are cumbersome and take days to complete. Not to mention the risks and safety permits involved with manually walking or climbing structures.
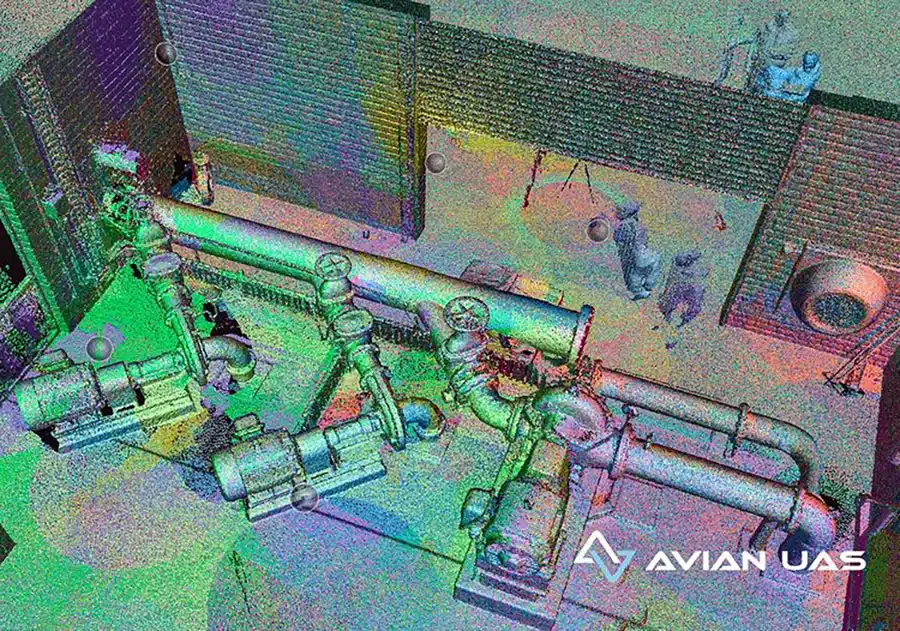
Generate 3D maps and models
One of the most significant advantages of using UAVs for surveying is: that you can create 2D maps and 3D models. Our world is built in 3D yet we often design and build in traditional (and outdated) 2D methods. The benefits of using 2D maps and 3D models is better awareness of site context and local environments, greater transparency of project status, increased visibility of site operations and improved methods of team collaboration and stakeholder communication. You get so much more rich data when using UAVs in the construction project lifecycle.
Faster to deploy and safer
Drones are faster to deploy than using manual inspection methods like rope access or elevated work platforms. Plus, the drone can quickly change position to obtain a better view of the site, asset or building to get greater visibility of the current conditions.
Accessible across different terrains
LiDAR surveys use millions of laser measurements to obtain topographical details. Using standard drones will not measure natural surface or see through trees and vegetation to reveal the natural surface. Thickly vegetated or forested areas would require LiDAR surveying.
The laser measurements are processed into a point cloud that can be used for feature extraction, breaklines and planimetric modelling.
Cost-effective and affordable
Drones are very affordable, convenient, and cost-effective when compared to other surveying and inspection techniques.
Drones reduce onsite risks and complete terrain mapping in faster time than using traditional surveyors walking the ground. This improves safety outcomes, site productivity and ensures that the client can optimize available resources.

Cons of UAV Surveys
Limited flight time
Drones can only fly for 20-30 minutes per battery. But professionals should possess the capability to power the drone for an entire day.
Susceptible to weather conditions
Most drones do not function appropriately on wet and windy (>40km/hr) days.
Requires licensing and insurance
In Australia, all drone pilots must have a CASA drone license and appropriate insurance to operate drones for commercial use.
Prone to accidents
Drones are still prone to accidents. They can crash, malfunction and cause property damage or injury to people.
Data theft and hacking
Drone data is susceptible to data theft and hacking; it’s important to take drone data security and protection measures seriously.
Legal issues
Drones cannot be operated over military bases, near airports or over people and crowded areas. There are a range of regulations when using drones that are listed on the CASA website.
The Bottom Line
Now that you have a good idea about UAV surveying and its various pros and cons, I am sure you can decide if you need to incorporate drones for your next project.
Contact our team of drone operators at Avian today to book a free consultation and site visit. We are a passionate team of land surveyors, geospatial experts and drone operators with ample AEC experience to handle medium to large-scale construction projects.


